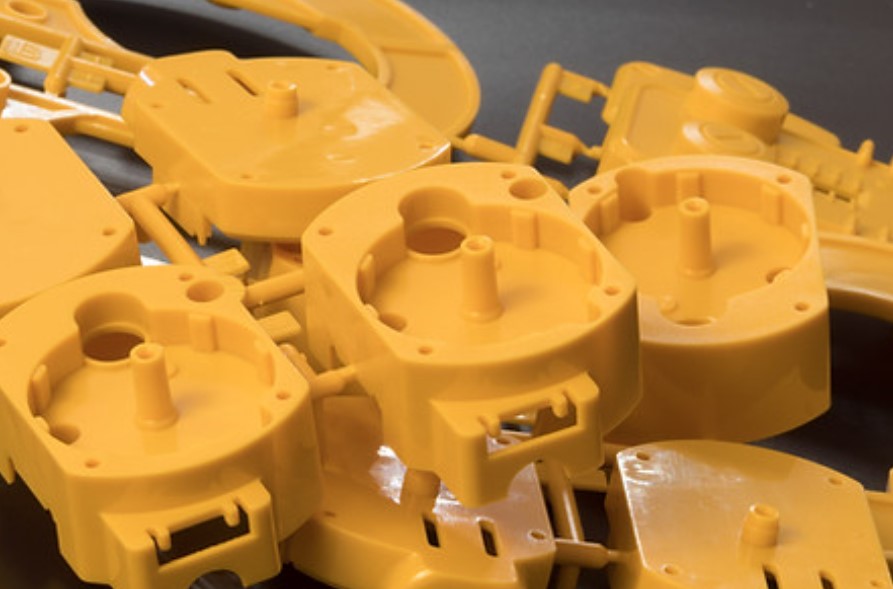
Injection moulding is a versatile and highly efficient manufacturing technology known for its ability to produce parts at high production rates. This process involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and intricate details with exceptional precision.
In addition to its precision, injection moulding offers consistent quality across large production runs, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing. The process also provides significant design flexibility and cost-effectiveness, enabling the production of detailed and reliable components at a competitive price point.
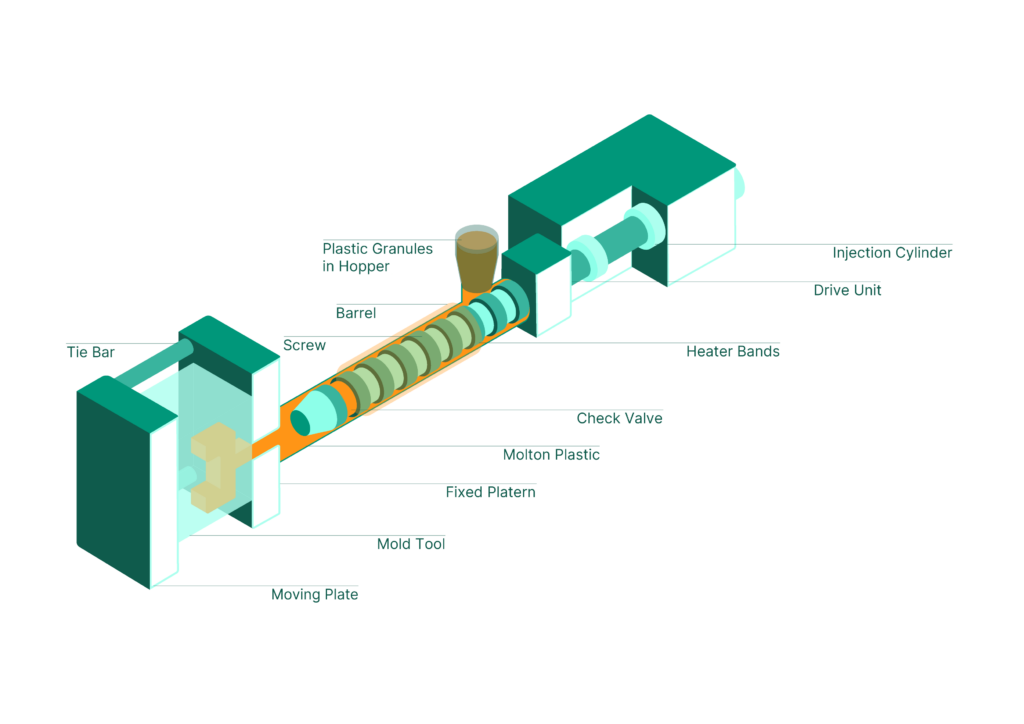
How Injection Moulding Works
First, a mold is meticulously crafted, typically from steel or aluminum, to shape the desired part. This mold is made up of two halves—the cavity and the core—both precisely machined to form the exact geometry needed for the part.
Once the mold is ready, thermoplastic pellets are melted and injected into the mold under high pressure. The molten plastic fills the cavity, conforming to the mold’s shape. After cooling and solidification, the mold opens, and the finished part is carefully removed for any necessary finishing touches.
Injection Moulding Use Cases
Injection moulding is widely used across various industries due to its ability to deliver high-quality components at a cost-effective rate. Its versatility and efficiency make it a preferred manufacturing solution for many applications.
In the automotive industry, injection moulding is essential for producing parts like dashboards, interior trims, and exterior body components. The consumer electronics sector relies on this technology to manufacture items such as smartphones, electronic housings, and other precision components.
Beyond these industries, sectors like aerospace, packaging, and consumer goods also leverage injection moulding to create custom parts and mass-produced products, benefiting from its ability to consistently deliver detailed and reliable components.
| Injection Moulding by the Numbers |
|---|
| Max Build Size: Up to several meters in the longest dimension Lead Times: Starting at 21 days Minimum Wall Thickness: max 0.05 mm (strongly dependent on material and boundary conditions) Dimensional Accuracy: +/- 0.1 % (minimum 0.1 mm) |
Source Industrial-Grade Injection Molded Parts
Painted

Painting offers an extensive array of color options, allowing you to choose the perfect shade to suit your needs. Beyond just color, different painting techniques and high-quality coatings can achieve a variety of finishes. Whether you’re aiming for a sleek glossy look, a sophisticated matte finish, a striking metallic sheen, or a unique textured surface, the right combination of paint and technique can bring your vision to life. This versatility makes painting an ideal choice for customizing and enhancing the appearance of products across various industries.
Polishing

This process involves the careful and gradual smoothing of the surface using a series of abrasive materials or compounds, each finer than the last. As the abrasives work their way across the surface, they remove imperfections and roughness, leaving behind a polished, glossy finish that not only enhances the visual appeal of the printed object but also brings out its fine details with greater clarity. The end result is a sleek, smooth surface that reflects light evenly, giving the object a refined and professional appearance, ideal for applications where aesthetics and surface quality are paramount.
Surface texturing

Surface texturing techniques are employed to create intricate patterns or textures on the surface of injection-molded parts, serving a variety of purposes that go beyond mere aesthetics. These textures can significantly enhance the functionality of the parts by improving grip, reducing glare, or adding tactile feedback. Additionally, surface texturing can be used to mimic natural materials, provide a unique visual appeal, or hide imperfections, making it a crucial step in customizing parts for specific applications. Whether aiming for enhanced usability or a distinct look, surface texturing adds both practical and decorative value to injection-molded components.
Pad printing
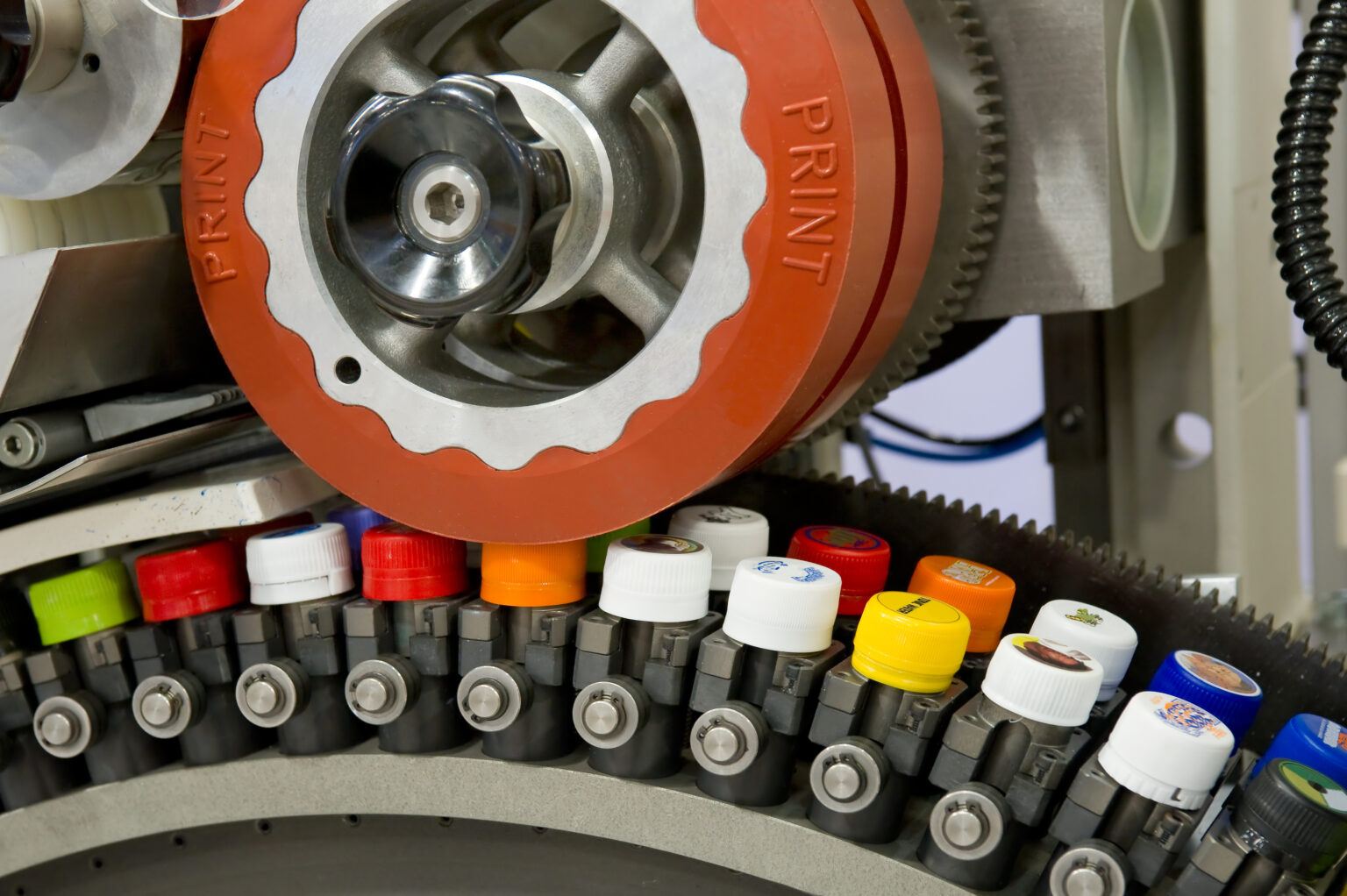

Pad printing is a precise and versatile technique used to apply detailed designs, logos, or markings onto the surface of injection-molded parts. This process involves transferring ink from an etched plate onto the part using a specially designed printing pad, which conforms to the shape of the surface, ensuring even coverage and sharp, clear images.
The pad’s flexibility allows it to reach areas that might be challenging for other printing methods, making it ideal for adding intricate details to complex geometries and curved surfaces. Whether you’re adding branding, product information, or decorative elements, pad printing ensures that the final design is both durable and visually striking, enhancing the overall appearance and functionality of the part.
Source Industrial-Grade Injection Molded Parts
D2PCNC offers flexible solutions for sourcing parts tailored to your needs. With fast quotes and on-demand manufacturing, you can quickly order parts with ease. For large or complex orders, our team of experts collaborates with you to develop, align, and oversee a comprehensive manufacturing quality plan, ensuring your project is expertly managed from start to finish.
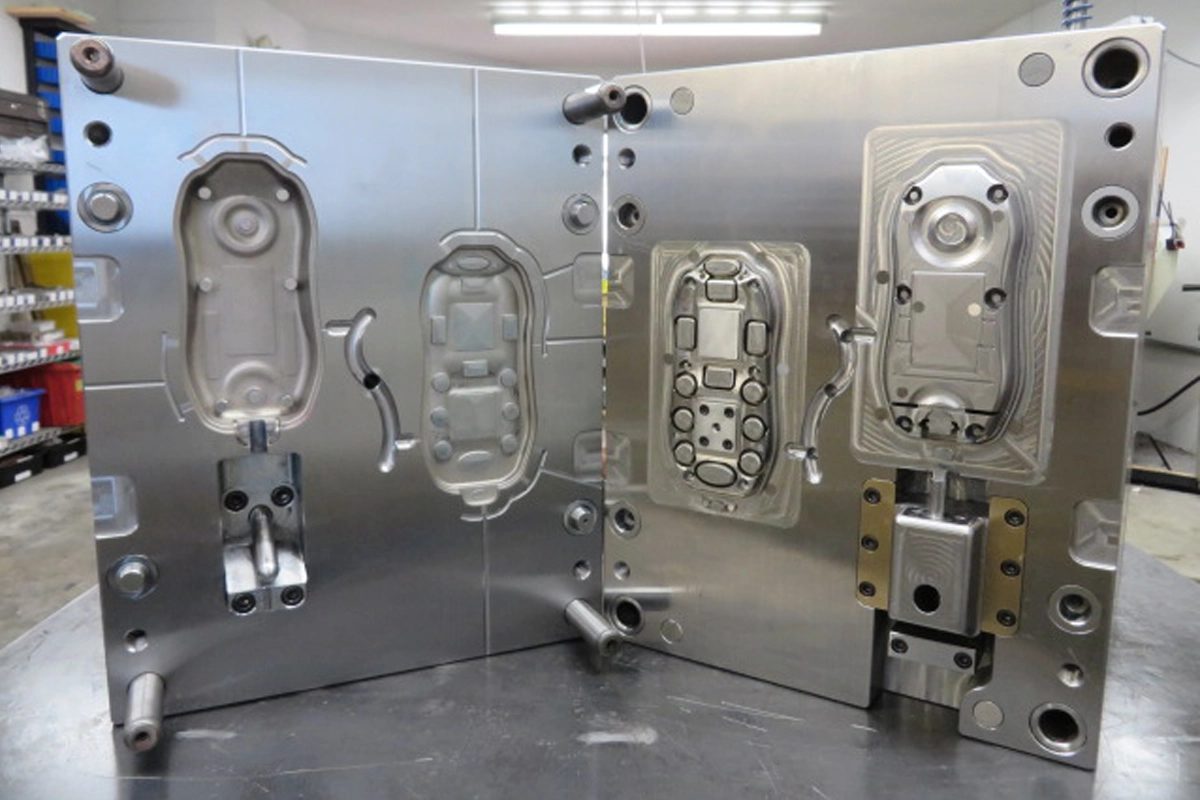

On-Demand Manufacturing
- Instant quoting and DFM checks
- Short lead times
- Fast and intuitive order placement
Production Orders
- Expert support from end-to-end
- Comprehensive manufacturing and quality plan
- Guaranteed quality meeting advanced specifications
Popular Injection Moulding Materials
Injection moulding provides a variety of epoxy resins that serve as equivalents to the thermoplastic materials used in other manufacturing processes. Some of the most popular options include:
| Popular Injection Moulding Materials |
|---|
| ABS: ABS, or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, combines strength and durability with low weight and a high load capacity. The material provides a good compromise between mechanical properties, cost, and accuracy. Thanks to its versatility and affordable price, ABS is used widely used across industries. PA: PA, or polyamide, provides excellent mechanical properties. Its high ductility and impact strength make it interesting for functional parts in various industries such as automotive. Typical usage would be interior parts for automotive, functional prototypes, and in the medical industry. PC: Polycarbonate (PC) combines good mechanical properties such as impact resistance, strength, rigidity, and hardness. It can also withstand high temperatures and offers high dimensional stability. PC is typically used for cases of any kind. PP: Polypropylene (PP) offers high strength and toughness combined with a light weight. This material also has low moisture absorption. PP is a relatively inexpensive material often used in everything from electronic components to everyday household goods, such as storage containers. Elastomers (such as TPU): TPU and other elastomers offer high elasticity or shock absorption. These materials are often used for energy-absorbing parts produced for safety – such as helmets. |


