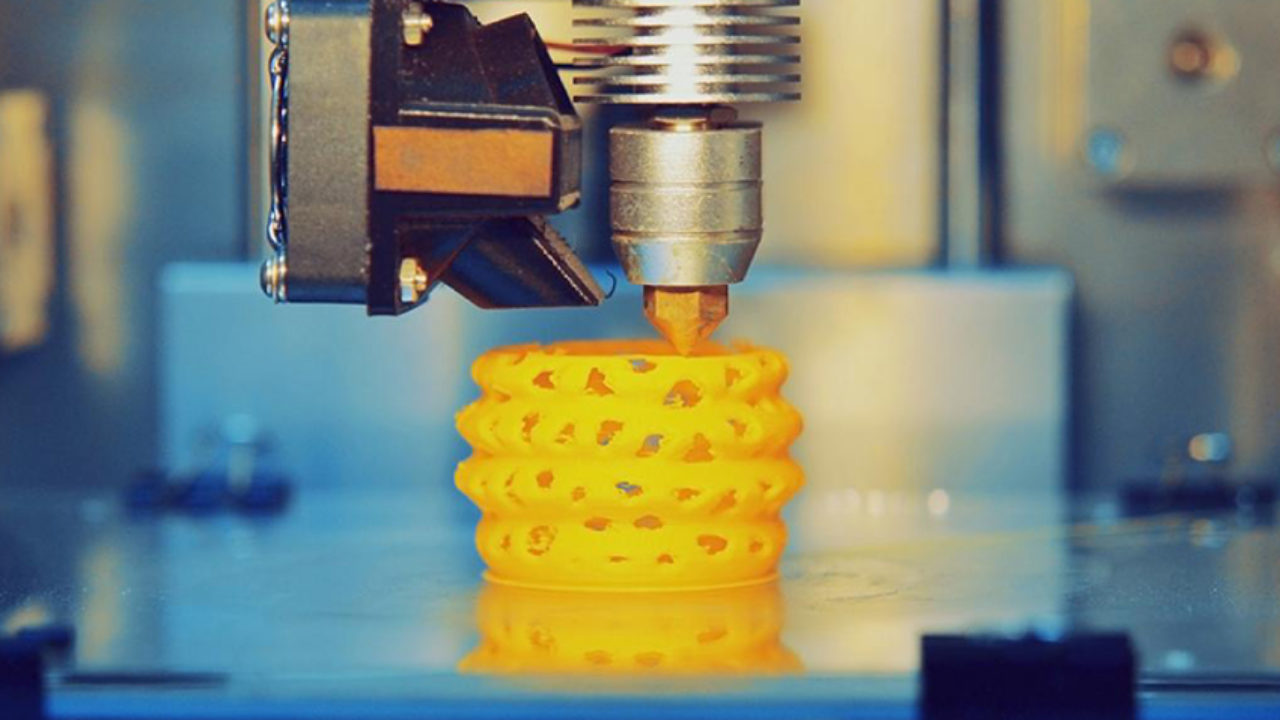
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a widely accessible and cost-effective additive manufacturing technology, making it a popular choice for both prototyping and production. Its ease of use and affordability, coupled with the quick turnaround times, allows for rapid iterations and efficient production, even for small batches.
This flexibility is further enhanced by the diverse range of materials compatible with FDM, from basic thermoplastics to high-performance engineering polymers. This versatility ensures that FDM can cater to a broad spectrum of applications, making it a valuable tool across various industries.
How FDM Works
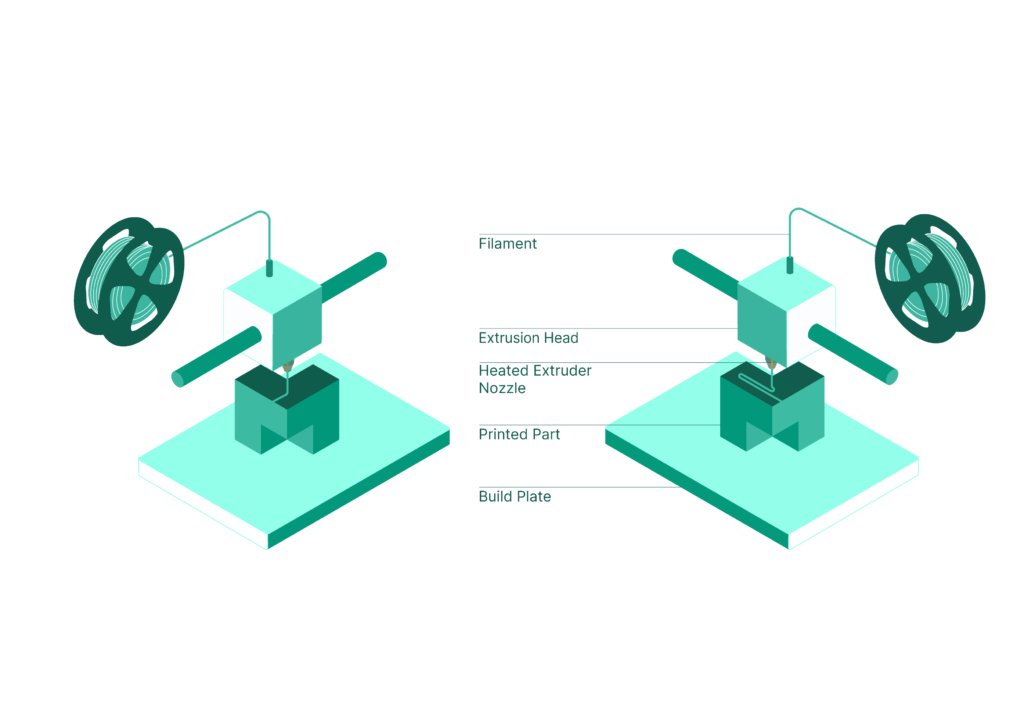
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is an additive manufacturing process that creates parts from thermoplastic materials. The process involves a heated, movable nozzle that extrudes plastic filament, which is heated above its melting point. As the filament is extruded, it is deposited layer by layer onto the previous layers, fusing together as it cools. This sequential layering process continues until the entire part is fully formed, resulting in a solid and precisely manufactured plastic component.
FDM Use Cases
At D2PCNC, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a go-to technology for rapid and functional prototyping, offering a practical solution for projects requiring quick visual and geometric assessments. This additive manufacturing method is particularly valued for its ability to create precise prototypes that help designers and engineers evaluate form, fit, and function before moving into full-scale production. The flexibility of FDM allows us to produce prototypes with complex geometries, ensuring that every detail of the design is accurately represented.
Beyond prototyping, FDM at D2PCNC is also well-suited for manufacturing end-use parts, especially when the production requirements are low-volume. This makes it an ideal choice for small-batch manufacturing, where the cost-effectiveness of FDM plays a significant role in delivering high-quality parts without the need for extensive tooling or long lead times. The versatility of materials available for FDM further enhances its appeal, allowing us to meet specific material properties required for different applications.
Specific use cases at D2PCNC include the production of jigs, fixtures, and components for specialized fields such as art, architecture, and model-making. These applications benefit from the precision and durability of FDM-produced parts, which can withstand the demands of real-world use while maintaining aesthetic and functional integrity. Whether for a detailed architectural model or a custom jig for assembly processes, FDM provides a reliable and efficient solution tailored to the unique needs of each project.
| FDM by the Numbers |
|---|
| Max Build Size: 914 x 610 x 914 mm (standard size) Lead Times: Starting at 6 days Minimum Wall Thickness: 1.0 mm (depending on material and geometry) Standard Color: Various Dimensional Accuracy: +/- 0.4% with a minimum of 0.4 mm |
Available FDM Finishes

Smoothed
During the smoothing process, a chemical reaction reworks the plastic component. The top layer of the part is dissolved using a medium in a solution bath, resulting in a very smooth surface.

Painted
Painting can significantly enhance the design of your printed part or provide a clearer evaluation of a printed prototype by improving its appearance and highlighting details.

Sanded
Sanding is used to smooth the part and eliminate visible blemishes, such as support marks or excess material. The type of sandpaper selected depends on the layer height and print quality of the part, ensuring a refined finish.

Color dyed
The plastic component is immersed in a water bath. The resulting chemical reaction causes the dye to penetrate the part.

Sealed
The sealing process involves using an aqueous solution to close the outer surface and fill in small pores. Depending on the geometry of the part, the sealing solution is either manually applied or the part is dipped into the solution.
Key Feature: High-Performance Materials
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is known for producing high-performance parts that exhibit exceptional strength, toughness, and impact resistance. This technology is particularly advantageous for applications requiring durable and robust components, making it a reliable choice for industries that demand high structural integrity.
In addition to its mechanical capabilities, FDM excels in creating flame-retardant parts that comply with stringent certification standards across industries such as aerospace, rail, and electronics. Thermoplastics like ULTEM 1010 and ULTEM 9085 are prime examples of materials used in FDM that offer superior flame retardancy, ensuring safety and performance in critical applications. These materials allow for the production of parts that not only meet but exceed the rigorous requirements of these specialized sectors.
Source Industrial-Grade FDM parts
D2PCNC offers flexible solutions for sourcing parts tailored to your needs. With fast quotes and on-demand manufacturing, you can quickly order parts with ease. For large or complex orders, our team of experts collaborates with you to develop, align, and oversee a comprehensive manufacturing quality plan, ensuring your project is expertly managed from start to finish.

On-Demand Manufacturing
- Instant quoting and DFM checks
- Short lead times
- Fast and intuitive order placement
Production Orders
- Expert support from end-to-end
- Comprehensive manufacturing and quality plan
- Guaranteed quality meeting advanced specifications
Popular Materials for FDM
Curious about the ideal material for your project? Explore our interactive technology and material advisor to discover the best options.
| Popular Materials for FDM |
|---|
| ABS-ESD7: ABS-ESD7 is a durable ABS material blended with carbon, providing electrostatic discharge (ESD) properties. This unique feature prevents static electricity buildup, making it ideal for applications where ESD protection is crucial. ABS-ESD7 is commonly used in the electronics industry for components like electronic fixtures, housings, and customized packaging. It’s also preferred in environments with a heightened risk of explosions from sparks, such as fuel tank parts and packaging for hazardous materials. Lead time is 6 days. ABS-M30: ABS M30 is a modified acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) known for its strength, durability, and lightweight with high load capacity. It offers an excellent balance of mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and accuracy, outperforming conventional ABS. This makes it ideal for loaded functional prototypes, production gears, jigs, fixtures, and manufacturing tools, as well as form and fit testing. Its versatility and affordability have made ABS M30 a widely used material across various industries. Lead time is 6 days. ABS-M30i: ABS M30i offers high strength, durability, and low weight, similar to ABS M30, but with the added advantage of biocompatibility according to ISO 10993 and USP Class VI standards, allowing it to be sterilized. This makes it ideal for applications where biocompatibility and sterilization are essential, such as surgical aids, medical devices, and manufacturing tools in the food industry. It’s also suitable for parts that come into contact with skin. ASA: ASA filament is a versatile thermoplastic similar to ABS but with enhanced mechanical properties, a better surface finish, and superior UV resistance. Available in 10 different colors, ASA is ideal for a range of applications, particularly outdoor use due to its UV resistance. It’s commonly used for industrial-grade polymer prototypes, aesthetic consumer goods, and in the automotive industry, where both durability and appearance are key. Onyx: Onyx is a micro carbon fiber-filled nylon known for its exceptional mechanical properties, including strength, toughness, and chemical resistance. Its durability and appealing appearance make it a popular choice for both consumer and industrial applications, particularly for end-use parts. PC: Polycarbonate (PC) is known for its excellent mechanical properties, including impact resistance, strength, rigidity, and hardness, alongside high temperature and dimensional stability. These characteristics make it suitable for applications like jigs and fixtures, cases, and visual models. The standard lead time for PC parts is 6 days. PC-ABS: PC-ABS is a versatile material that combines the temperature resistance of polycarbonate (PC) with the flexural strength of ABS, making it highly durable with excellent impact strength, particularly at low temperatures. This blend is ideal for solid tools and functional prototypes, and it is frequently utilized in the automotive and electronics industries. The typical lead time for PC-ABS parts is 6 days. ULTEM® 1010: ULTEM 1010 is a high-performance thermoplastic polyetherimide (PEI) known for its superior heat resistance, tensile strength, and chemical resistance. It also has the lowest coefficient of thermal expansion among all FDM materials, making it ideal for demanding and specialized applications. ULTEM 1010 is commonly used for high-strength jigs, lightweight composite tooling, and, in its certified grade, for food contact production tools and customized medical applications. Typical lead time for ULTEM 1010 parts is 8 days. ULTEM® 9085: ULTEM is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional strength, making it a viable alternative to metals. Its flame-retardant properties make it especially valuable in the aviation and rail industries. Additionally, PEI-based ULTEM is low in toxicity, making it suitable for medical and food-related applications. Typical lead time for ULTEM parts is 8 days. |