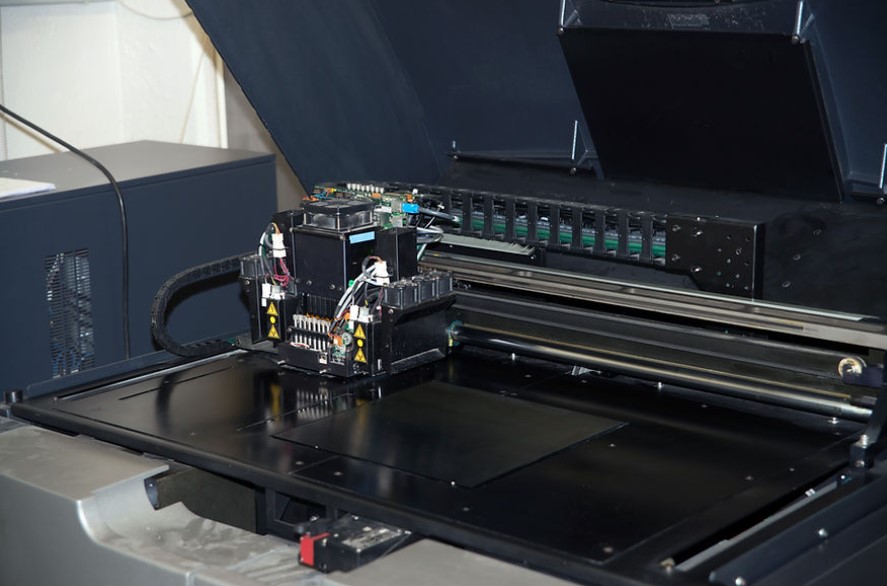
PolyJet printing, also known as material jetting, is a cutting-edge 3D printing technology renowned for its exceptional detail and ultra-smooth surface finishes. This process utilizes multiple jets to deposit fine layers of photopolymer resin, which are then cured with UV light to create highly accurate and intricate parts.
The technology excels in producing complex geometries and vivid colours with precision, making it ideal for applications where both aesthetic quality and functional performance are crucial. Its ability to print in multiple materials simultaneously adds to its versatility, allowing for the creation of parts with varying properties within a single build.
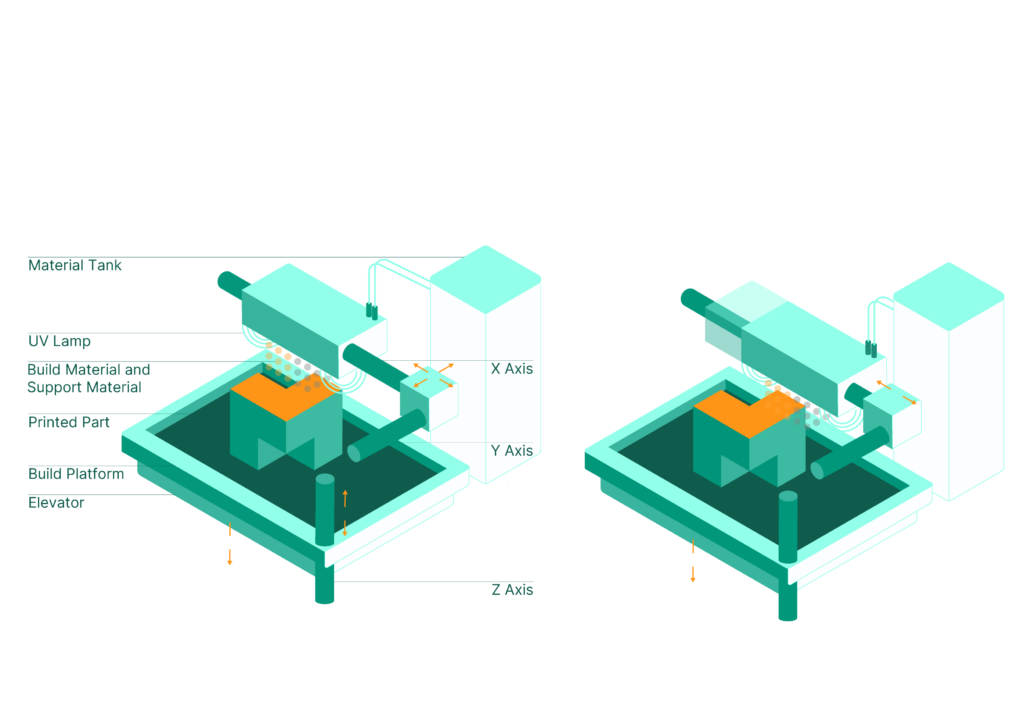
How PolyJet Works
A standout feature of PolyJet printing is its ability to simultaneously print with multiple materials, enabling the creation of objects with diverse material properties and intricate colour combinations. This capability allows for the production of parts with varying textures, flexibilities, and colours within a single build, offering unparalleled design flexibility.
The PolyJet printing process begins with the deposition of ultra-thin layers of liquid photopolymer materials onto a build platform. This is achieved through multiple print heads that jet these materials in a manner similar to inkjet printers, ensuring precise and consistent layer application.
Once each layer is deposited, it is immediately cured using UV light to solidify the material. This rapid curing process ensures that the parts are built with high precision, capturing fine details and intricate features while maintaining a smooth and flawless surface finish.
PolyJet Use Cases
PolyJet printing is extensively utilised across various industries, particularly in product design and development. This technology excels in creating parts with intricate details and smooth surfaces, making it ideal for comprehensive visual evaluations and functional testing. Its capability to produce a wide array of colours further enhances the ability to assess designs before full-scale production.
Additionally, PolyJet printing is highly effective for small-batch production and custom components featuring complex geometries. The technology’s unique advantage lies in its ability to print with multiple materials simultaneously, offering the flexibility to integrate different material properties within a single print run. This versatility makes it an excellent choice for creating parts with varied characteristics tailored to specific applications.
| PolyJet by the Numbers |
|---|
| Max Build Size: 250 x 250 x 150 mm Lead Times: Starting at 10 days Minimum Wall Thickness: 0.8 mm (depending on material and geometry) Dimensional Accuracy: +- 0.1 % (minimum 0.1 mm) |
Popular SLA Finishes

Sanded
By methodically sanding the surface with a range of sandpaper grits, rough areas, layer lines, and support marks can be effectively smoothed out. This process results in a more polished and visually appealing part, providing a refined finish that facilitates easier painting and clear coating.

Painted
PolyJet parts can be produced in a range of colours, but painting offers further customization options. Following printing, parts can be primed and painted to achieve specific colour requirements and enhance their visual appeal.

Polishing
This process involves progressively refining the surface with abrasive materials or compounds, ultimately achieving a glossy finish that accentuates the fine details of the printed object. The careful smoothing enhances the object’s overall appearance and clarity, bringing out its intricate features.
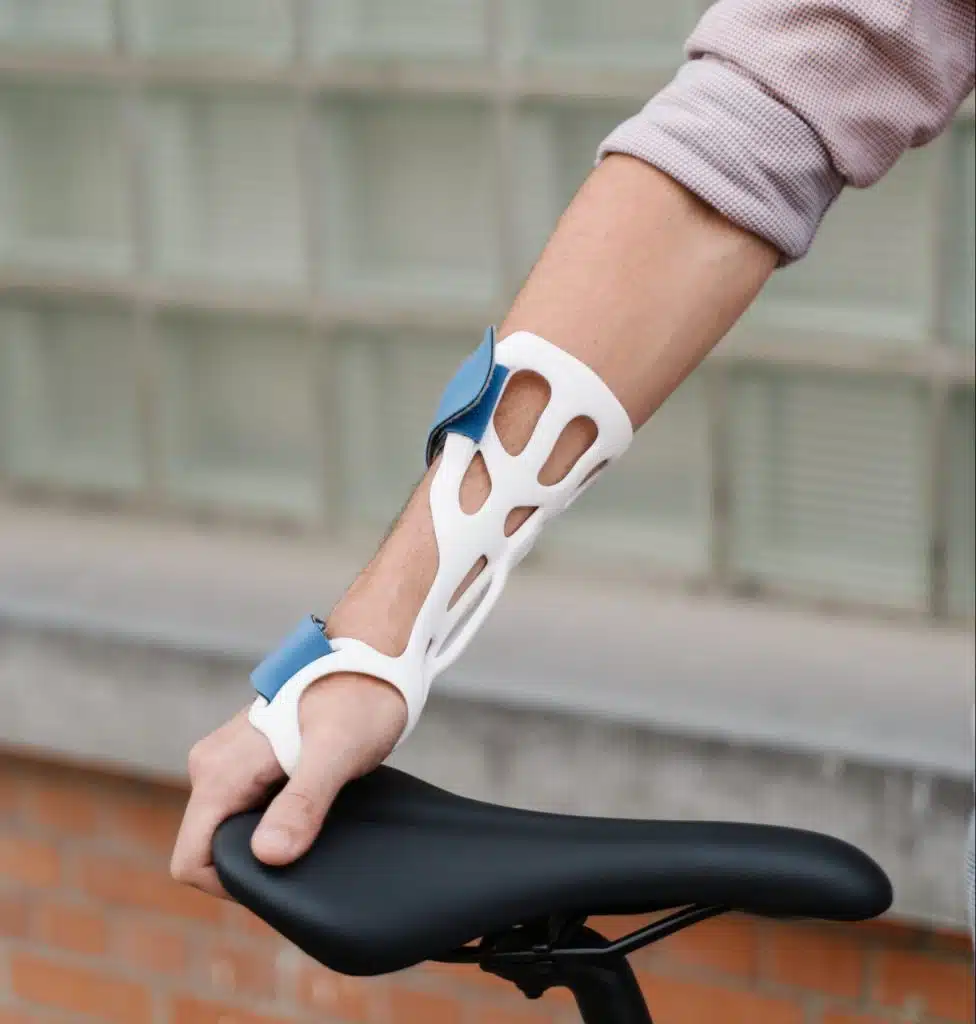
Clear coating
The application of a transparent layer provides a glossy finish that not only elevates the aesthetic appeal of the part but also offers protection against scratches and environmental elements. This clear coating enhances the polish of decorative or display objects, ensuring they maintain their visual appeal and durability over time.
Source Industrial-Grade PolyJet parts
D2PCNC offers unparalleled flexibility for sourcing parts to meet your specific needs. Obtain instant quotes and place orders swiftly through our on-demand manufacturing services. For complex projects, our team of experts will collaborate closely with you to create, align, and oversee a comprehensive manufacturing quality plan from inception to completion.

On-Demand Manufacturing
- Instant quoting and DFM checks
- Short lead times
- Fast and intuitive order placement
Production Orders
- Expert support from end-to-end
- Comprehensive manufacturing and quality plan
- Guaranteed quality meeting advanced specifications
Popular PolyJet materials
PolyJet provides a diverse selection of epoxy resins that serve as equivalents to the thermoplastics used in other manufacturing technologies. Among the most popular choices are:
| Popular PolyJet materials |
|---|
| ABS Plus: ABS Plus is a versatile thermoplastic renowned for its strength, durability, and impact resistance. It surpasses standard ABS materials with improved dimensional stability, as well as enhanced heat and chemical resistance. This makes ABS Plus ideal for a range of applications, including prototyping, functional testing, and the production of end-use parts. Medical/Biocompatible materials: Medical and biocompatible materials are specifically engineered to meet rigorous regulatory standards for medical and healthcare applications. These materials undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they are safe and compatible with the human body. They are commonly used in the production of medical devices, surgical guides, and anatomical models, where safety and precision are paramount. Rigid materials: Rigid materials are known for their exceptional stiffness, strength, and dimensional stability, effectively mimicking the properties of traditional engineering plastics. They demonstrate strong resistance to impact, heat, and chemicals. These materials are widely used in diverse industries for applications ranging from engineering prototypes to end-use parts, where durability and precision are essential. Rubber-like materials: Rubber-like materials are designed to simulate the properties of elastomers, offering exceptional flexibility, elasticity, and tear resistance. They come in various hardness options, making them versatile for different applications. These materials are widely used in industries including footwear, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, where flexible, durable components are essential. |